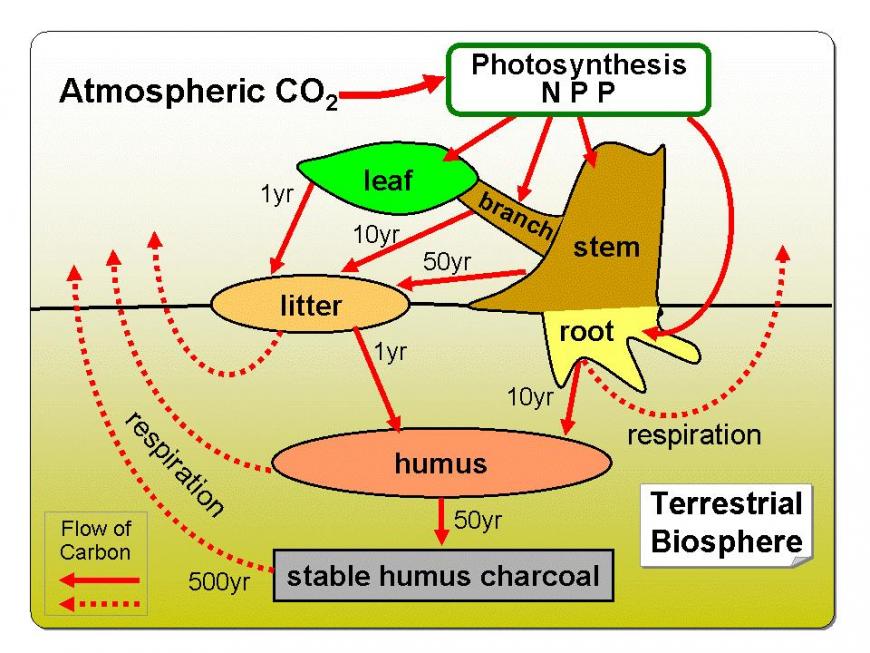
Carbon exchange in terrestrial ecosystems
Green plants absorb atmospheric carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and transform it to organic carbon through photosynthesis, using the energy of sunlight. About half of the carbon photosynthesized by plants is returned to the atmosphere as CO2 through plant respiration. The remainder is incorporated in living leaves, stems, and roots. Plant residues deposited on or within the soil are decomposed by a range of organisms. The ultimate product of organic matter decay in the soil is a relatively stable complex of compounds known as humus.