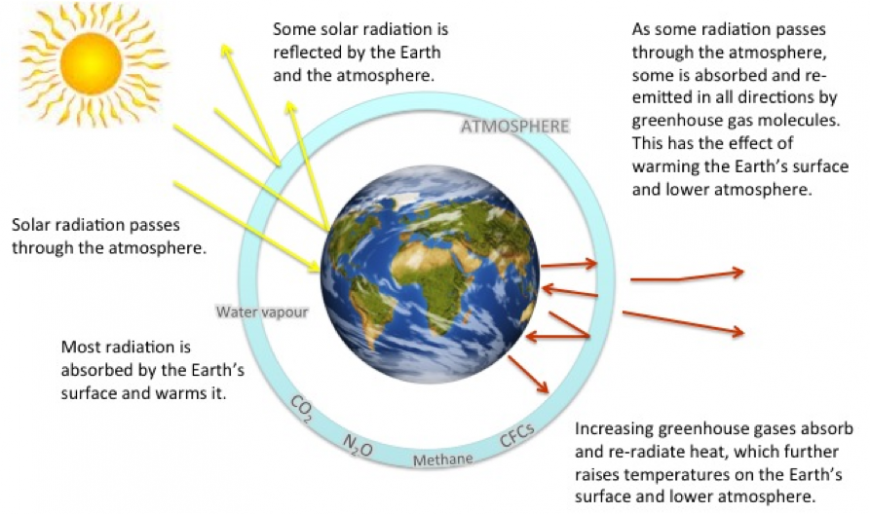
What is the greenhouse effect?
Human activities such as burning fossil fuels, intensive farming, and cutting down forests produce greenhouse gases. These gases – mostly carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide – play an important role in regulating the temperature of the earth’s atmosphere. They accumulate in the atmosphere, enfold the earth and trap the sun's heat. The more greenhouse gases are emitted, the faster the world's climate will warm up. This process is often called ‘global warming’. However, it is better termed ‘climate change’ as it is likely to bring about more extreme events, such as floods, storms, droughts and landslides, rather than an increase in temperature only.